Processing and Milling
Rice in its natural form is inedible. Therefore, milling and processing of the Rice is required for attaining the desired quality of Rice. In our Rice mills, we process the Rice for making it polished and edible. The main goal of milling is the removal of Barns and Hulls from the Rice so that its consumption becomes possible. Rice is the basic primary product obtained from Paddy after Paddy is processed. Here are some of the operations done to create the final product.
Drying and Paraboiling:
The exposure of paddy to gradual drying processes and controlled temperatures reduce the unneeded moisture prevalent in the paddy.These can dry 40 tons of Paddy per hour. We ensure taking appropriate care so that none of the delicate portion of the Rice breaks while processing.
Exposure of Rice grains to steam for removal of Hull and Barn layer is known as Parboiling. We, MRV Group, have a committed Parboiling plant furnished with soaking bins that are specially designed for handling the temperature of the water. Clarity required-taste and aroma get hampered because of the usage of the normal water-should it be usage of the water.
Here are the steps involved in Drying and Paraboiling:
- Precleaning Cleaning is a material separation process. The objective is to separate undesirable foreign materials from the paddy and leave a cleaned paddy for storage and processing.
- Pre Steam Drying Paddy is Dried to maintain uniform Moisture level before Treating with Steam.
- Steaming Use of steam for gelatinizing the starch is preferred to other methods of heating as it does not remove any moisture from the rice. Paddy is subjected to steam.
- Drying Drying paddy is a process of removing moisture from the grain; it is often called moisture extraction. Drying is required because after Steam Treatment paddy is at a relatively high moisture level—up to 26%—and This is done with artificially heated air.
- Halting Paddy is Stored in Storage bins for about 24 hours, to reduce to stress on the grains.

Milling:
The last and the final step of the overall procedure is the Milling. In this step the seed grains are made to get exposed to varied sophisticated machines like Paddy Separators, De-Huskers, Graders, Precision Sizers, De-Stoners, Pre-Cleaners, etc. Our aim is to provide you with the Rice of exceptional quality, well refined and nutritious having perfect aroma.Here are the steps involved in Miling:
Pre cleaning Although paddy grain may have gone through a cleaner before drying. Cleaning paddy prior to husking and whitening is crucial in attaining high milling recoveries.

The de-stoner is an important component of the rice mill, The grain gathers a lot of stones and mudball during handling, which must be removed. The de-stoner is a simple vibrating deck and air blower that suspends the grain from the stones. The stones are thrown off in one end and the paddy in the other end.

Husking or de-hulling is a process for removing the rice hull from the rough rice. We use rubber roller husker.
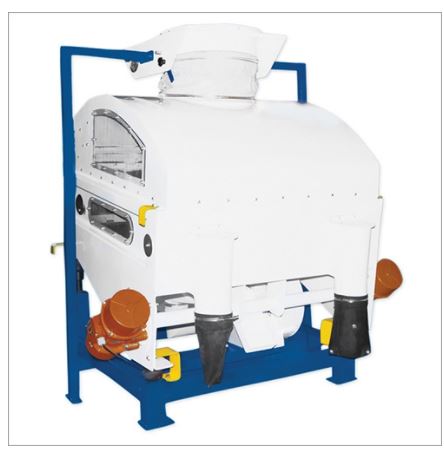

In order to separate the remaining unhusked paddy grains from from the brown rice fraction and feed them back into the husker a paddy separator is used.

White rice is produced from brown rice by removing the bran layer and the germ. The bran layer is removed from the kernel by applying friction to the grain surface rubbing the grains against an abrasive surface. The amount of bran removed is normally between 8-10% of the total paddy weight but this will vary according to the variety and degree of whiteness required.

Mist polisher is employed to brush off remaining bran dust and to create a characteristic gloss on the milled rice. In mist polishers, a controlled amount of water mist is injected, resulting in highly polished grain. Mist polishing improves the storability of milled rice because of the complete removal of the bran.

The major step in the modern milling process is the removal of the brokens from the milled rice, Length grading separates “head rice” from large brokens. Blending stations allow for mixing of head rice and brokens in the correct proportion, as specified by the grade standards. For instance, premium grade rice in the India allows for 95% head rice and 5% brokens.
Automated separation of grains based on color and surface texture.

Milled rice is marketed in bags, and therefore bagging stations from an integral part of the modern rice mill. The sizes of the bags depend on the requirements of the customer. In our mills, milled rice is packaged in plastic / Non Woven bags of 25, 35 and 50kg, and packaging is fully mechanized

